Given the position vectors of vertices A, B and C of ΔABC are \(\vec a,\vec b\) and \(\vec c\) respectively.
D is point on BC with position vector \(\vec d\)such that AD is the bisector of ∠A. I is the incenter of ΔABC.

Observe from the figure that D divides BC in the ratio BD : DC.
Using the angular bisector theorem, we know that the angle bisector of an angle in a triangle bisects the opposite side in the ratio equal to the ratio of the other two sides.

Recall the vector \(\vec{AB}\) is given by
\(\vec{AB}\) = position vector of B - position vector of A

Similarly, \(\vec{AC}=\vec c-\vec a\)
So, we have

Recall the position vector of point P which divides AB, the line joining points A and B with position vectors \(\vec a\) and \(\vec b\) respectively, internally in the ratio m : n is

Here, we have D dividing BC internally in the ratio m : n where m = BD = \(|\vec a-\vec b|\) and n = DC = \(|\vec c-\vec a|\)

Suppose

From angular bisector theorem above, we have
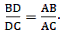
Adding 1 to both sides,

In addition, as CI is the angular bisector of ∠C in ΔACD, using the angular bisector theorem,
we have


So, I divides AD in the ratio (β + γ):α.
Let the position vector of I be \(\vec {\text x}\).
Using the aforementioned section formula, we can write

Thus, \(\vec d=\cfrac{\beta\vec b+\gamma\vec c}{\beta+\gamma}\) and the position vector of the incenter is \(\cfrac{\alpha\vec a+\beta\vec b+\gamma\vec c}{\alpha+\beta+\gamma},\) where \(\alpha=|\vec b-\vec c|,\beta=|\vec c-\vec a|\) and \(\gamma=|\vec a-\vec b|.\)