The sums of n terms of two A.P`s are in ratio \(\frac{3n + 5}{5n +7}\)
Let a1 and d1 be the first term and common difference of the first A.P, respectively. Similarly let a2 and d2 be the common difference of the second A.P, respectively. According to the given condition.


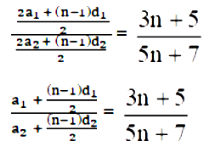
Now the Nth term is given by a + (N–1) d Equating the coefficients
\(\frac{(n-1)}{2}\) = N -1
⇒ n = 2N – 1
