Public finance is one of the most important branches of economy. It highlights the role and functions of the government Government has to perform various functions like protection from external attack, generation of employment, protection of property, maintaining law and order, provision of collective needs, etc.
To perform these functions efficiently, any government needs finance which can be received from various sources. Public finance deals with the study of principles of income and expense of the government.
The structure of public finance can be explained as follows:
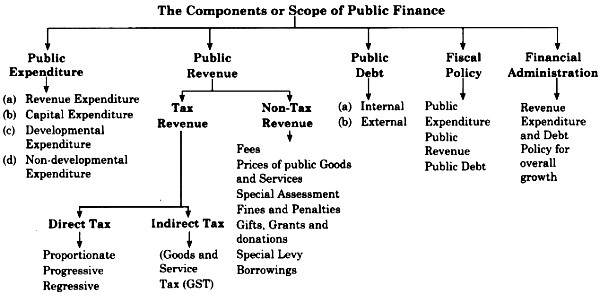
The Components or Scope of Public Finance:
(A) Public Expenditure : It refers to that expenditure which is incurred by the public authority (Central, State and Local Government) for promoting economic and social welfare of a country.
Public expenditure is classified as follows:
(a) Public Expenditure : It refers to expenditure on day-to-day functioning of the government. E.g. administration cost, salary allowances and pensions of government employees, etc. It is incurred regularly but it does not create any assets to government.
(b) Capital Expenditure : It refers to the expenditure for the development of a country. E.g. investment by government in projects, provision of infrastructure, repayment of loan, etc. It does not incur regularly but it makes addition to the assets of the economy.
(c) Developmental Expenditure : It refers to that expenditure of the government, which gives productive impact to the economy. It results into generation of employment, increase in production, etc.
(d) Non-developmental Expenditure : It refers to that government expenditure which does not yield any direct productive impact on the economy. E.g. war expenditure.
It is unproductive in nature.
(B) Public Revenue : It refers to aggregate collection of income with the government through various sources.
They are classified as:
(a) Tax Revenue
(b) Non-tax Revenue
(a) Tax Revenue : There are two types of taxes collected by the government.
They are as follows:
Direct tax : Direct tax is that tax which is paid by a person on whom it is legally s imposed. E.g. income tax, wealth tax, etc.
Direct tax can be proportionate – (constant rate of tax on all incomes), progressive (rate of tax increases with an increase in income) or regressive (rate of tax declines ) with rise in income. In India, we have progressive tax rate system.
Indirect tax : Indirect tax is that tax which ( is imposed on one person but can be paid by the other, e.g. GST.
A taxpayer cannot shift the burden of direct tax to others, however, in case of indirect tax, tax burden can be shifted to others.
(b) Non-tax Revenue : Non-tax revenue refers to the revenue received by the government from various sources other than taxes.
Public expenditure is an important aspect which is incurred by the public authority (central, state and local government). Public expenditure is required for the protection of the citizens of a country, for satisfying social needs or collective needs and for promoting social and economic welfare of the people in a country.
Classification of public expenditure is as under:
(1) Revenue expenditure : It is the expenditure of the government to carry out day-to-day functions. It is recurring in nature. It does not create any assets to government It consists of administrative expenditure, interest payment, pensions and salaries to government employees, etc.
(2) Capital expenditure : It refers to the expenditure of the government for the development of a country.
It consists of huge investment in different developmental projects, repayment of government loans, investment on land, building, machines, etc.
It is non-recurring in nature:
(3) Developmental expenditure : The expenditure which results in generation of employment and price stability, it is known as developmental expenditure.
It consists of expenditure on education, social welfare, industrial development, etc. It leads to an increase in production. It is s productive in nature.
(4) Non-developmental expenditure : It is that government expenditure which does not yield any direct productive impact on the economy. It is mainly in form of expenses on administration costs, war expenses, etc. It is unproductive in nature. It is observed that, since last 30 years, there is a tremendous growth in the total public expenditure of a country because modern government performs many functions for the social and economic development of a country.
(C) Public Debt:

Tax is a major source of revenue to the Government:
According to Prof. Taussig, “The essence of a tax as distinguished from other charges by government is the absence of a direct ‘quid pro quo’ (benefit) between the tax payer and the public authority. ”
Prof. Seligman states that, “a tax is a compulsory contribution from a person to the government, without reference to special benefits confessed. ”
Thus, every citizen of a country is legally bound to pay tax.
Tax is imposed on income, property or commodities and services.
Types of Taxes :
(1) Direct Tax : It is paid by the tax payer on his income and property. A tax-payer cannot transfer the burden of direct tax to others. Impact and incidence of direct tax falls on the same person. E.g. Income tax, wealth tax, etc.
Direct taxes are further classified into three categories.
(i) Proportionate tax
(ii) Progressive tax
(iii) Regressive tax
(2) Indirect Tax : It is levied on goods and services. It is paid at the time of production or sale and purchase of a commodity or a service.
The burden of indirect tax can be shifted by the tax-payer (producers) to other persons.
Hence, impact and incidence of tax are on others. E.g. GST.
Thus, major share of public revenue is the contribution by tax revenue in India.
(D) Fiscal Policy : It is the means through s which government adjusts its spending’s c and tax rates. It helps to monitor and influence nation’s economy. It deals with public expenditure, public revenue and l public debt.
Thus, it is the financial policy implemented by the government.
(E) Financial Administration : It implies I an efficient implementation of revenue, external and debt policy of the government. It includes preparation and implementation of the government budget along with overall economic growth of a country.
Budgetary actions of the government affect production, size and distribution of income and utilization of material and human resources of a country. Thus, the scope of public finance is important in a modern economy.