NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths Chapter 12 - Heron's Formula
1. A traffic signal board, indicating ‘SCHOOL AHEAD’, is an equilateral triangle with side ‘a’. Find the area of the signal board, using Heron’s formula. If its perimeter is 180 cm, what will be the area of the signal board?
Solution:
Let each side of the equilateral triangle be a.
Semi-perimeter of the triangle,

2. The triangular side walls of a flyover have been used for advertisements. The sides of the walls are 122 m, 22 m and 120 m (see Fig). The advertisements yield an earning of ₹5000 per m2 per year. A company hired one of its walls for 3 months. How much rent did it pay?

Solution:
Let the sides of the triangular will be
a = 122m, b = 12cm, c = 22m
Semi-perimeter, \(s = \frac {a + b + c}2\)
\((\frac{122+ 120 + 22}4)m = \frac{264}2 m = 132 m\)
The area of the triangular side wall

Rent for 1 year (i.e. 12 months) per m2 = Rs. 5000
∴ Rent for 3 months per m2 = Rs. 5000 x \(\frac3{12}\)
= Rent for 3 months for 1320 m2 = Rs. 5000 x \(\frac3{12}\) x 1320 = Rs. 16,50,000.
3. There is a slide in a park. One of its side walls has been painted in some colour with a message “KEEP THE PARK GREEN AND CLEAN” (see Fig). If the sides of the wall are 15 m, 11 m and 6 m, find the area painted in colour.

Solution:
Let the sides of the wall be
a = 15m, b = 11m, c = 6m
Semi-perimeter,

Thus, the required area painted in colour
= 20√2 m2
4. Find the area of a triangle two sides of which are 18 cm and 10 cm and the perimeter is 42cm.
Solution:
Let the sides of the triangle be a = 18 cm, b = 10 cm and c = x cm
Since, perimeter of the triangle = 42 cm
∴ 18cm + 10 cm + x cm = 42
x = [42 – (18 + 10)cm = 14cm
Now, semi-perimeter, s = \(\frac{42}2\) cm = 21 cm

Thus, the required area of the triangle = \(21\sqrt{11}\) cm2
5. Sides of a triangle are in the ratio of 12 : 17 : 25 and its perimeter is 540 cm. Find its area.
Solution:
Let the sides of the triangle be
a = 12x cm, b = 17x cm, c = 25x cm
Perimeter of the triangle = 540 cm
Now, 12x + 17x + 25x = 540
⇒ 54x = 54 ⇒ x = 10
∴ a = (12 x 10)cm = 120cm,
b = (17 x 10) cm = 170 cm
and c = (25 x 10)cm = 250 cm
Now, semi-perimeter, s = \(\frac{540}2\)cm = 270 cm
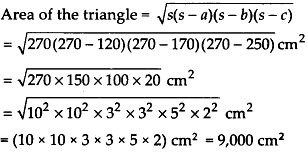
6. An isosceles triangle has perimeter 30 cm and each of the equal sides is 12 cm. Find the area of the triangle.
Solution:
Let the sides of an isosceles triangle be
a = 12cm, b = 12cm, c = x cm
Since, perimeter of the triangle = 30 cm
∴ 12cm + 12cm + x cm = 30 cm
⇒ x = (30 – 24) = 6
Now, semi-perimeter, s = \(\frac{30}2\)cm =15 cm

Thus, the required area of the triangle = 9√15 cm2
7. A park, in the shape of a quadrilateral ABCD, has ∠C = 90°, AB = 9m,BC = 12m,CD = 5m and AD = 8 m.
How much area does it occupy?
Solution:
Given, a quadrilateral ABCD with ZC = 90°, AB = 9 m, BC = 12 m, CD = 5 m and AD = 8 m.
Let us join B and D, such that ABCD is a right angled triangle.

Now, to find the area of ∆ABD, we need the length of BD.
In right-angled ∆BCD, by Pythagoras theorem
BD2 = 502 + CD2
⇒ BD2 = 122 + 52
⇒ BD2 = 144 + 25 = 169
⇒ BD = 13 m
Now, for ∆ABD, we have
a = AB = 9 m, b = AD = 8 m, c = BD = 13 m

∴ Area of quadrilateral ABCD = area of ∆BCD + area of ∆ABD
= 30 m2 + 35.5 m2
= 65.5 m2 (approx.)
8. Find the area of a quadrilateral ABCD in which AB = 3 cm, BC = 4 cm, CD = 4 cm, DA = 5 cm and AC = 5 cm.
Solution:
Given a quadrilateral ABCD with AB = 3 cm, BC = 4 cm, CD = 4 cm, DA = 5 cm and AC = 5 cm.

For ∆ABC, a = AB = 3 cm, b = BC = 4 cm and c = AC = 5 cm

Now, area of quadrilateral ABCD = area of ∆ABC + area of ∆ACD
= 6 cm2 + 9.2 cm2
= 15.2 cm2 (approx.)