From the first equation of motion for constant acceleration, plot the v-t graph. From the second equation of motion for constant acceleration, plot the x-t graph.
Since the acceleration of the ball during the contact is different from ‘g’, we have to treat the downward motion and the upward motion separately.
For the downward motion: a = g = 9.8 m/s2 ,

The ball reaches the ground when x = 19.6 m. This gives t = 2 s. After that it moves up, x decreases and at t = 4 s, x becomes zero, the ball reaching the initial point.


During the next two seconds the ball goes upward, velocity is negative, magnitude decreasing and at t =
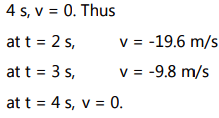
At t = 2 s there is an abrupt change in velocity from 19.6 m/s to -19.6 m/s. In fact this change in velocity takes place over a small interval during which the ball remains in contact with the ground.

Acceleration: The acceleration is constant 9.8 m/s2 s throughout the motion (except at t=2s).