Construction:
Cyclotron consists of two-semicircular disc-like metal containers (which are as the letter D), D1 and D2, which are called dees. Figure (a) shows the view of a cyclotron. The diameter of these dees is


approximately same and are placed at very small interval. The cyclotron uses both electric and magnetic fields in combination to increase the energy of charged particles. As the fields are perpendicular to each other they are called ‘crossed fields’.
Inside the metal boxes the particle is shielded and is not acted on by the electric field. The magnetic field, however acts on the particle and makes it go around in a circular path inside a dee. Every time the particle moves from one dee to another. It is acted upon by the electric field. The whole assembly is evacuated to minimise collisions between the ions and the air molecules. A high frequency alternating voltage is applied to the dees. Magnetic field acts perpendicular to the plane of dees.
Working: A radio frequency oscillator generates approximately 104 V voltage and 106 Hz frequency alternating voltage. Positive ions or positively charged particles (as protons) are released at the centre P. They move in a semi-circular path in one of the dees and arrive in the gap between the dees in a time interval T/2; where T is the period of revolution.
As shown in the figure when any charged particle enters the dees from the ion source then due to the perpendicular magnetic field it does motion in a circular path. Suppose at any instant t, D1 is positive and D2 is negative and positive ion completes its semi-circular path in D1 and moves towards D2 and its energy increases by qV. The time taken by the particle to do motion in D1 is T/2. The alternating voltage in a cyclotron is so adjusted that as any charged particle completes its semicircular path in a dee; the polar effect of the alternating voltage changes. The particle also does motion in a circular path in D2 due to the perpendicular magnetic field. In this way a charged particle does two times motion in a magnetic field in one cycle and its energy increases by 2qV. As energy increases, the radius of the circular path also increases, hence the time period is kept constant.
The frequency of the applied voltage is so adjusted that the polarity of the dees is reversed in the same time that it takes the ions to complete one half of the revolution. The requirement is called resonance condition.
The ions are repeatedly accelerated across the dees until they have the required energy to have a radius approximately that of the dees. They are then deflected by a magnetic field and leave out the system via an exit slit.
Mathematical Analysis:
The necessary centripetal force for the circular path of the particle in a cyclotron is obtained from the perpendicular magnetic field;

The value of this frequency should be equal to the frequency of applied alternating voltage. Hence, this is also called cyclotron frequency.
Angular frequency of the cyclotron
ω = 2πv = \(\frac{q B}{m}\) …………. (5)
It is clear from the equation (2), (4) and (5) that the time period, time in semi-circle and angular frequency of charged particle in a cyclotron are constant. (For constant value of B) i.e., they are not dependent on the speed of the particle and radius of the path.
Kinetic energy of the particle

When the radius of the circular path is same as the radius of the dees, then the kinetic energy is maximum of the particle.
Hence, from equation (7);
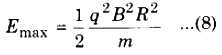
If total number of circular cycles are N and V is applied potential difference. Gained energy in one complete cycle is 2qV, then the total kinetic energy in N cycles will be :
E = N × energy in one cycle
E = N × 2qV = 2qVN ………… (9)
On comparing equations (8) and (9)
