In common language, work is a word defining any action in which physical labour is involved. But the definition changes in Physics. If force is applied on anybody and that body is displaced in the direction of the applied force, then it is said to be work is done.
(a) Work Done by Constant Force
For doing work always force is required. When force applied on any object it changes the position of

the object. Then work done is defined as the product of the component of force in the direction of the displacement and the displacement; or vice versa, i.e
Work = Force × Displacement in the direction of force.
If the applied force on a body is F then the body is displaced from the position A to position Band d is the displacement then the work done in: W=Fd
Unit and dimensional formula:
∴ W = Fd
∴ Unit of work = Nm = Joule (J)
If F = 1N, d = lm then W = 1J
Hence the applied force on the body is 1 Newton and body is displaced 1 meter due to this force, then the work is said to be one joule.
∵ W=Fd
∵ Dimensional formula of work
= [M1L1T-2] [L]
= [M1L2T-2]
(b) Work Done by Constant Force Acting at an Angie e Suppose an object (a body) is kept on a horizontal plane. A force F i applied at an angle θ from the horizontal on the body; which displaces the body on the horizontal plane from position A to R The distance from A to B is d. The displacement generated is due to the horizontal component Fcos θ. Hence, the work done is:

W = Force x Displacement in the direction of force
=Fcosθ × d
or W = Fdcosθ
or \(W=\vec{F} . \vec{d}\)
i.e., Scalar product of force and displacement provides work.
Work Done by the Variable Force
In the position of the variable force; suppose the work done at point P by a force \(\vec{F}\) and displacement \(\vec{dr}\) is
\(\begin{aligned} d W &=\vec{F} \cdot \vec{d} r \\ \text { or } & d W=F d r \cos \theta \end{aligned}\)
Here, e is the angle between  and
and 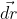 at point P.
at point P.
The value of 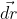 is infinitely small.
is infinitely small.

Hence, work done for infinitely small displacement dr is dW.
Similarly, to calculate the work done for complete distance A→b R, the total distance is divided into \(\Delta \vec{r}_{1}, \Delta \vec{r}_{2}\) …………. These should be so small that the force relative to them can be considered constant. If the forces relative to these are \(\vec{F}_{1}, \vec{r}_{2}, \vec{r}_{3}\) ……………….. respectively, then work done in the total displacement:

The total work done is given mathematically as;

Calculation of Work Done by The Force-Displacement Graph
For calculation of work done by graphical procedure it is assumed that the force and displacement are in the same directions. Suppose, the change in force with the displacement (from A to B) is same as in fig. The initial position of the body is r1 and final position ìs r2.

The distance r is assumed to be made of various small elements dr1, dr2 ,dr3, ………….. etc. The force component can be assumed to have a constant value Δr for displacement Δr. Thus, total work done will be;

Thus, the work done by the force can be determined by measuring the area between the curve and the displacement axis.