Three basic tissue systems in flowering plants are:
1. Epidermal tissue system: It consists of
- Epidermis
- Cuticle and wax
- Stomata
- Trichomes
2. Ground tissue system: It consists of
- Cortex
- Endodermis
- Pericycle
- Medullary rays
- Pith
- Ground tissue of leaves
3. Vascular tissue system: It consists of (i) Xylem (ii) Phloem
The Epidermal Tissue System:
Originate from the outermost layer of apical meristem. Forms the outermost covering of various plant organs which remains in direct contact with the environment. Performs manyfold function eg. Protection, absorption, excretion, secretion, gaseous exchange and control of transpiration etc.
1. Epidermis:
Epidermis (Greek, Epi = upon; Derma = skin) is generally uniseriate, i.e., composed of single layer of epidermal cells.These cells are of varying shapes and size and form a continuous layer interrupted by stomata. Sometimes they are separated by intercellular spaces (in petals of some flowers). In some cases epidermis may be multilayered eg.
Ficus, Nerium, Peperomia. The epidermis of Ficus elastica leaf is two layered and that of Peperomia pereskiaefolia is multilayered (13-14 layers).
The epidermal cells are living and may contain chloroplasts (shade plants, water plants, some ferns)., anthocyanin pigments, tannins, oils and crystals The cells are parenchymatous and living. The outer tangential walls are usually thicker as compared to inner tangential walls. Each cell has a large central vacuole and a peripheral thin cytoplasm. Certain epidermal cells of some plants or plant parts are differentiated into variety of cell types.
- In aerial roots, the multiple epidermal cells are modified to velamen, which absorb water from the atmosphere.
- Some of the cells in the leaves of grasses are comparatively very large, called bulliform or motor cells. They are thin-walled and contain big central vacuoles filled with water. They play an important role in the folding and unfolding of leaves.
- Some members of Gramineae and Cyperaceae possess two types of epidermal cells the long cells and the short cells. The short cells may be cork cells or silica cells


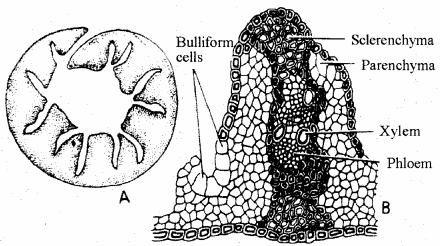
2. Cuticle and Wax:
Cuticle is a fatty substance (cutin) deposited over the outer surface of epidermal cells in the form of a separate layer. It is absent in young roots. The cuticle layer may be thin or thick and smooth or rough. Structurally a cuticle layer consists of cellulose lamellae interrupted with pectic substances and cutin. Usually the cuticle is covered with wax which may be deposited in the form of granules, rods, crusts or viscous semi liquid masses. Other substances, deposited on the cuticle surface may be. oil resin, silicon and salts (calcium oxalate or calcium carbonate).
3. Stomata:
Singular of stomata is stoma (Greek, stoma=mouth). A typical stoma is microscopic and usually consists of two kidney-shaped guard cells surrounding a pore. The guard cells are usually, much smaller in size as compared to other epidermal cells. They are, therefore, rapidly affected even by a small change in turgor.
The stomatal pore is generally elliptical in surface view. The dimension of stomatal pore varies from species to species, but on an average, it measures about 20 pm long and about 10-20 pm wide when fully open. In some species the guard cells are surrounded by subsidiary cells or accessory cells which differ morphologically from the other epidermal cells.
The guard cells generally have thick walls towards pore and thin walls on opposite side. Moreover, the cellulose micelles in guard cell walls are oriented radially rather than laterally. The guard cell walls have special elastic properties. The adjoining cell walls of two guard cells around pore are free and not attached with each other. These properties help them to stretch laterally during stomatal opening.
Basic functions of stomata include exchange of gases with atmosphere, transpiration and regulation of temperature In dicot plants maximun number of stomata are found in lower surface and either stomata are absent are few on upper surface, these leaves are called Hypostomatous. In monocots, equal no. of stomata are found on both surfaces and these leaves are called Amphistomatous. Stomata are absent in aquatic plants. Stomata are sunken in xerophytes.