Modification for Storage of Food – Stoage Roots:
In some plants, the primary’ tap roots are modified for storing reserve food materials. The secondary roots remain thin and they are absorptive in function. The storage roots are usually swollen and assume various Roots are modified into different forms to perform specific functions other than their normal functions. Modification in
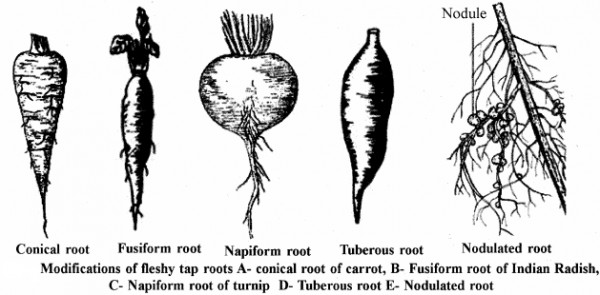
- Conical: The swollen root is broad at the base and tapers gradually towards the apex giving a shape of cone, e.g., Carrot.
- Fusiform: The root is swollen in the middle and narrow towards both its base and apex giving a shape of spindle, e.g., Radish. Half or less than half portion towards the base of fusiform root is formed by hypocotyl.
- Napiform: The root is nearly globular or spherical in shape. The basal portion of root is much swollen which suddenly tapers towards the apex giving a top – shaped appearance, e.g., Turnip (Brassica napus, vern. Shazgam) and Beet (Beta vulgaris, vern. Chukandar).
- Tuberous: The storage root having no definite shape is called tuberous, e.g., Mirabilis jalapa (4 O’clock plant), Trichosanthes (vem. Par-wal), Echinocystis Zobata (The tuberous root is lobed and weighs as much as 22 kg.).
 4
4
Modifications of Adventitious Root:
1. Roots modified for storage of food:
- Tuberous roots: Some of the adventitious roots store food materials and become swollen. They arise singly and do not attain a definite shape, e.g., Sweet potato (Ipomoea batata). The tubers of sweet potato also bear adventitious buds and behave as reproductive roots. They arise from the nodes of running stem.
- Fasciculated roots: The swollen tuberous roots, when occur in clusters, are called fasciculated roots. Examples are – Dahlia, asparagus, etc. In Dahlia, cluster of tuberous roots he at the base of stem. In asparagus, the fleshy roots occur at intervals on the normal roots.
- Palmate tuberous roots: Some fleshy roots are palmate in shape, called palmate tuberous roots. In some orchids, they appear as palm of human hand.
- Nodulose roots: The adven – titious roots swell only near their apices like single beads, e.g., Mango, ginger (Curcuma amada), Cosuts speciosus, etc.
- Moniliform roots: These roots are alternately swollen and constricted giving a beaded appearance, e.g., Dioscorea alata, Basella rubra (Indian spinach vem. Kulfa), Momordica charantia (Bitter gourd), etc.
- Annulated roots: These thickened roots look as if formed by a number of discs placed one above another, e.g., Ipecac (Psychotria ipecacuanha)
