Special tissues:
These tissues perform special function in the plants e.g secretion of resin gum, oil and latex.
These tissues are of two types:
- Glandular tissue
- Laticiferous tissue.
Glandular tissues:
As the name indicates this tissue is present in the form of glands in or on various parts of plants. A gland is a specialized group of cells that are endowed with the capacity to secrete or excrete products. These are of two types:
- External glands,
- Internal glands.
1. External glands: They generally occur on the epidermis of stem and leaves as glandular outgrowth e.g glandular hair, nectar secreting and enzyme secreting glands.
(a) Glandular hair: These hair are present in epidermal layers of leaves and are of various kinds. They may be unicellular or multicellular. They are living e.g. Stinging hair on the under surface of Urtica dioica (Bichhu buti) is unicellular arising from lower epidermis of leaf. The walls of these hair are slicified, calcified and brittle. Contents of hair are poisonous and are secreted by a gland at the base of hair. When struck sharply the hair rupture the skin like hypodermic needle. The hair injects an albuminoid poison and causes irritation and blisters.
(b) Nectaries: Present in flowers or leaves. In Rutaccae they are found as a disc below the ovary. In Euphorbia pulcherrima the nectaries on the edge of involucere are composed of layer of elongated palisade like secrected cells. Cell walls of these cells are thin and the cells have dense cytoplasm.
(c) Digestive glands or Enzyme seereting glands: Insectivorous plants posssess the power of digesting proteins from bodies of insects by secreting some digestive enzymes by means of glands or glandular hair e.g drosera (sundew).

(2) Internal glands: These are of several types
- Oil glands: In cirus cinensis (orange) the internal glands secrete a volatile oil into a central reservoir.
- Resin glands: In Pinus the resin secreting cells form one or two peripheral layers that surround a schizo- genously developed canal or duct in the leaves and stem.
- Water secreting glands: (Hydathodes water stomata) These excrete water in the form of drops (found in leaves of some herbacious angiosperms that generally grow in humid.places. Hydathodes are present at the tip of leaves of som plants e.g colocasia or along margin (Tropaeoleum). They are present at the end and veins are always open and of large size.
Hydathode have an aperture guarded b guard cells. Below the aperture is an air cavity. Below which is a loose tissue calle epithem. Epithem is made of thin walled colourless cells with intercellular spaces filled with water. Below the epithem are terminal tracheids representing the end conducting tissue.

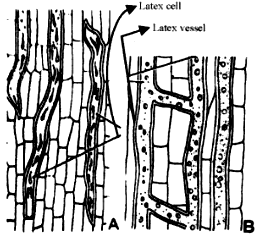
Laticiferous tissue:
This tissue is mainly composed of thin walled elongated, branched and multinucleate tube like structures that contain colourless milky or yellow coloured juice calle latex. They are scattered throughout the ground tissue of the plant and contai stored organic matter in the form of starch, rubber, tannins, alkaloids, mucilage enzymes, protein etc. This tissue is of two types:
- Latex cells
- Latex vessels
(1) Latex cells: They differ from latex vessels in that they are not formed due to cell fusions and with other latex cells to form a network. They are branched or unbranched. They do not anastamose e.g Calotropis, Nerium, Thevetia.
(2) Latex vessels: They are composed of a large number of cells placed end to end with their transverse walls dissolved so as to form a long vessels. They are unbranched in the beginning but get branched later. Two or more latex vessels fuse with each other forming a network e.g. Papaver, Argemone, Sonchus.