A metallic bar PQ of length l, mass m and resistance R is placed on a frictionless metal rails of negligible resistance inclined at an angle θ above the horizontal. The uniform magnetic field B is in direction as shown in figure. The metallic bar is released from rest and slides down the rails and finally attains terminal velocity.
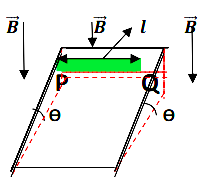
(1).The terminal velocity of the bar is :
(a) \(\frac{mgR}{B^2l^2sin\theta}\)
(b) \(\frac{mgR\,sin\theta}{B^2l^2cos^2\theta}\)
(c) \(\frac{mgR\,cos\theta}{B^2l^2sin^2\theta}\)
(d) \(\frac{2mgR\,sin\theta}{B^2l^2cos^2\theta}\)
(2). The rate at which electrical energy is converted into heat energy in the bar after attaining terminal velocity is :
(a) \(\frac{B^2l^2v^2cos^2\theta}{R}\)
(b) \(\frac{B^2l^2v\,cos^2\theta}{R}\)
(c) \(\frac{B^2l^2v^2sin^2\theta}{R}\)
(d) \(\frac{B^2l^2vsin^2\theta}{R}\)