Let us consider two closely spaced equipotential surfaces A and B as shown in figure.
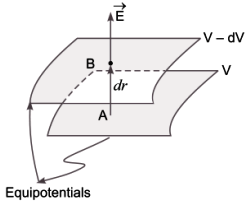
Let the potential of A be VA = V and potential of B be VB = V– dV where dV is decrease in potential in the direction of electric field \(\overrightarrow E\) normal to A and B.
Let dr be the perpendicular distance between the two equipotential surfaces. When a unit positive charge is moved along this perpendicular from the surface B to surface A against the electric field, the work done in this process is
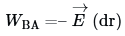
This work done equals the potential difference VA — VB
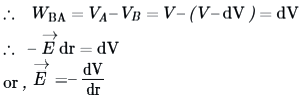
= negative of potential gradiant