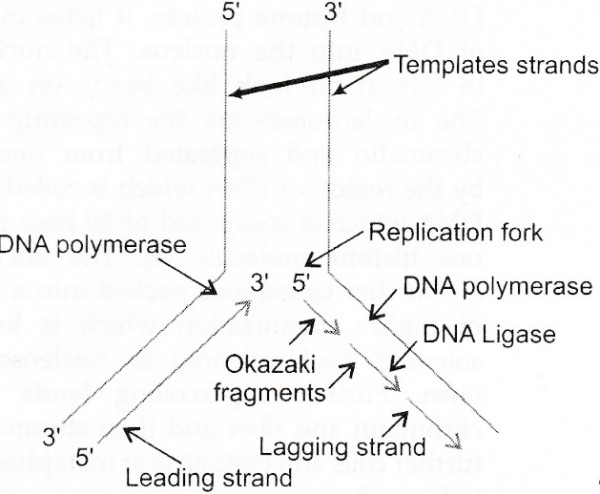
Process of DNA replication :
(i) The process of DNA replication begins at a point called the origin of replication (ori), to form a replication fork.
(ii) The separated strands act as templates for the synthesis of new strands.
(iii) DNA replicates in the 5' ---> 3' direction.
(iv) DNTPs (Deoxyribonucleoside-triose phosphates) act as substrate and also provide energy for polymerization of nucleotides.
(v) DNA polymerase is an enzyme that assembles a new DNA strand that is complementary to the template strand.
(vi) DNA polymerase continues to move along the template strand and add new nucleotides to the growing or complement any strand until the entire genome is replicated.
(vii) The DNA polymerase forms one new strand (leading strand) in a continuous stretch in the 5' ---> 3' direction (Continuous synthesis).
(viii) The other new strand is formed in small stretches (Okazaki fragments) in 5' ---> 3' direction (discontinuous synthesis).
(ix) The Okazaki fragments are then joined together to form a new strand by an enzyme, DNA ligase. This new strand is called lagging strand.