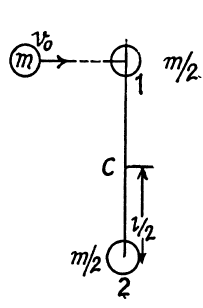
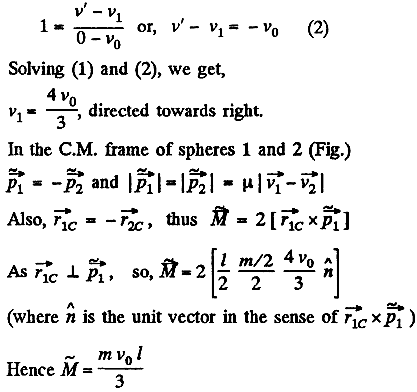From conservation of linear momentum along the direction of the incident ball for the system consists with colliding ball and phhere
mv0=mv'+m/2v1 (1)
where v' and v1 are the velocities of ball and sphere 1 respectively after collision. (Remember that the collision is head on).
As the collision is perfectly elastic, from the definition of co-efficient of restitution,