Total electric flux through any closed surface, is equal to 1/ε times the total charge enclosed by the surface.
ФE=∫E.dS=q/ε
Where ε is the permittivity of the medium (for free space ε=ε0),
So, ФE=∫E.dS=q/ε0
Where ∫E.dS is surface integral over the closed surface and q is the charge present in the closed surface S
The imaginary closed surface is called Gaussian Surface. If the surface encloses a continuous charge distribution then q is replaced by the intergal ∫ρdV,where ρ is the volume charge density.
Proof of gauss law of electrostatics:
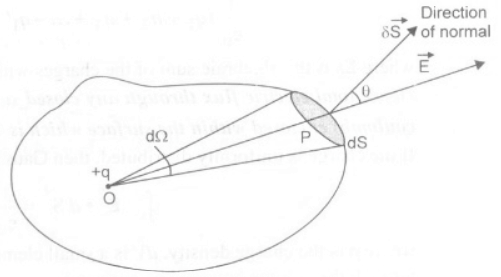
Consider a source producing the electric field E is a point charge +q situated at a point O inside a volume enclosed by an arbitrary closed surface S. let us consider a small area element ds around a point P on the surface where the electric field produced by the charge +q is E. if E is along OP and area vector dS is along the outward drawn normal to the area element dS.
Then the electric flux dФ through the area element dS is given by
dФ=E.dS=EdS cosθ
Where θ is the angle between E and dS and it is zero degree, therefore
dФ = EdS (1)
Since the source producing E at dS is a point charge +q at O, therefore
E=1/4πε0 q/(OP)2=1/4πε0q/r2 (OP=r)
Substituting this value of E in equation (1),we get
dФ=E.dS=q/4πε0dS/r2 .......(2)
Hence , total electric flux Ф through the entire closed surface S would be
∫dФ=q/4πε0 r2∫dS .......(3)
But ∫dS = 4πr2
Therefore, equation(3) becomes
Ф=∫E.dS= q4πε0 r2 /4πε0 r2
Or
Ф=∫E.dS= q/ε0 ......(4)
Equation (4) represents Gauss law for electrostatics for a single point charge. If the source producing the electric field has more than one point charges such as +q1,+q2,+q3,-q4.-q5,-q6………..etc,then the total flux due to all of them would be the algebric sum of all the fluxes as,
Ф=∫E.dS=1/ε0(q1+q2+q3-q4-q5-q6…….)
Or
Ф=∫E.dS=∑q/ε0
Hence proved a charge outside the Gaussian surface would contribute nothing to the electric flux.