Apparatus : A photoelectric cell G consists of the emitting electrode E (emitter) of the material being studied and the collecting electrode C (collector). The electrodes are sealed in an evacuated glass envelope provided with quartz window W that allows the passage of UV radiation and visible light. Monochromatic light of variable frequency from a suitable source S (such as a carbon arc) passes through a pair of polarizers P (permitting a change in the intensity of radiation) and falls on the emitter.
The electric circuit, as shown in below figure, allows the collector potential to be varied from positive through zero to negative with respect to the emitter, and permits the measurement of potential difference and current between the electrodes. When the collector is made negative, the voltmeter is connected in reverse.
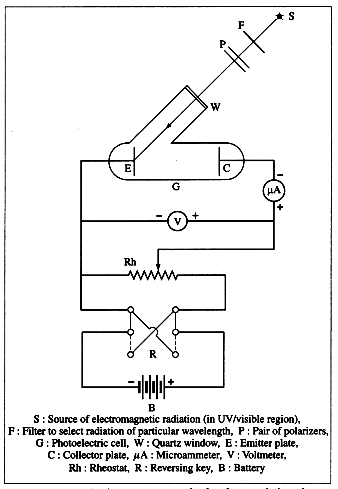
Apparatus to study the characteristics of photoelectric effect
[ Note : The radiation coming out of a filter is not truly monochromatic, it lies in the wavelength range between λ and λ + ∆λ that depends on the source and the filter. ]