1. Take a sheet of blank paper. Draw a line segment AC across the middle.
2. Draw another straight fine at right angles (90 degrees) to segment AC.
3. The second line should bisect segment AC at point B. We shall call this line as Normal. See in figure, (a)

4. Draw two lines from point B on the left side of the normal and two on the right side. The lines should be at angles of 30° and 60° respectively from the normal. Number these lines 1, 2, 3, 4 as shown in figure, (b)
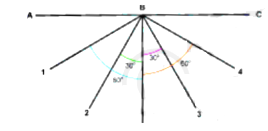
5. Place a mirror strip vertically on segment AC with its reflecting surface facing the normal.
6. See that the back of the mirror coincides with segment with a slit and let its light ray fall along line 4.
7. Now this ray is the incident ray for the mirror.
8. The angle between the normal and the incident ray is called the Angle of Incidence (∠i).
9. The angle between normal and the reflected ray (along line 1) is called the Angle of Reflection (∠r).
10. Adjust the mirror strip with the slit so that its light ray falls along line 3 and we find that the reflected ray falls along line 2.
11. Adjust the mirror strip with the slit so that its light ray falls along normal, then the angle of incidence is 0° (the angle between normal and incident ray “that is also normal here”, is 0°)
12. The reflected light reflects back along the normal itself.