The speed of sound, in gases, is given by
v = \(\sqrt{\frac{K}{ρ}}\)
where K = bulk modulus and ρ = density of gas
Using the Boyle’s law equation, (valid under isothermal conditions), PV = constant, along with the definition of bulk modulus

K = P (under isothermal conditions)
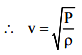
This formula, for the speed of sound in gases, was first given by Newton and is known as Newton’s formula for the speed of sound in air (and other gases)
Using the appropriate values for P and ρ , this formula gives the speed of sound, in air, under normal conditions, as close to 280 m/s. This value, however, is far too small compared to the experimentally determined value of v, which is close to 330 m/s.
It was Laplace who suggested that one needs to assume that the propagation of sound, through air, takes place under adiabatic (and not isothermal, (as assumed by Newton)) conditions. The appropriate equation is, therefore PVγ = constant (and not PV = constant). From this equation, we get

Hence the formula, for the speed of sound, takes the form

This formula gave a value of a v close to its experimentally measured value. It is, therefore, now taken as the accepted formula for the speed of sound in gases.