NCERT Solutions Class 10, Social Science, Political Science, Chapter 2, Federalism.
Exercises
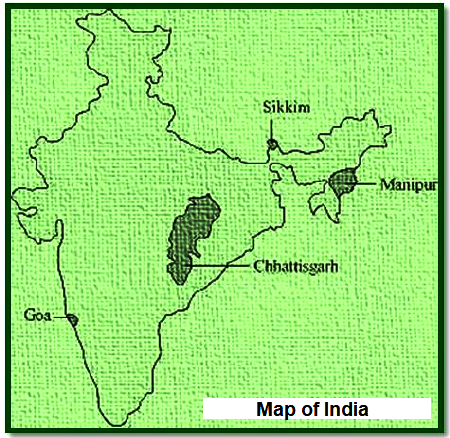
1. Locate the following States on a blank outline political map of India: Manipur, Sikkim, Chhattisgarh and Goa.
Solution:
2. Identify and shade three federal countries (other than India) on a blank outline political map of the world.
Solution:

3. Point out one feature in the practice of federalism in India that is similar to and one feature that is different from that of Belgium.
Solution:
In India, just like in Belgium, the central government has to share its powers with the regional governments. However, unlike India, Belgium has a community government in addition to the central and the state government.
4. What is the main difference between a federal form of government and a unitary one? Explain with an example.
Solution:
In a federal form of government, the central government shares its powers with the various constituent units of the country. For example, in India, power is divided between the government at the Centre and the various State governments.
In a unitary form of government, all the power is exercised by only one government. For example, in Sri Lanka, the national government has all the powers.
5. State any two differences between the local government before and after the Constitutional amendment in 1992.
Solution:
| Local governments Before 1992 |
Local governments After 1992 |
| Elections were controlled by the state and not held regularly. |
An independent State Election Commissionis responsible to conduct elections regularly. |
| Local governments did not have any powers or resources of their own. |
The State governments are required to share some powers and revenue with local government bodies. |
6. Fill in the blanks:
Since the United States is a ________ type of federation, all the constituent States have equal powers and States are _______vis-à-vis the federal government. But India is a _______ type of federation and some States have more power than others. In India, the _______ government has more powers.
Solution:
Since the United States is a coming together type of federation, all the constituent States have equal powers and States are strong vis-à-vis the federal government. But India is a together type of federation and some States have more power than others. In India, the Central government has more powers.
7. Here are three reactions to the language policy followed in India. Give an argument and an example to support any of these positions.
Sangeeta: The policy of accommodation has strengthened national unity.
Arman: Language-based States have divided us by making everyone conscious of their language.
Harish: This policy has only helped to consolidate the dominance of English over all other languages.
Solution:
I agree with Sangeeta's reaction. If the policy of accommodation was not followed, and states were not created on linguistic basis, there would have been further partition of India. For example, imposition of Hindi as the national language would have led the South to break away from the North and Tamil Nadu would have become an independent nation.