Conservation of biodiversity is the need of the hour. There are various reasons for conservation of biodiversity. There are two basic approaches of biodiversity conservation:
- In situ conservation (on site conservation)
- Ex situ conservation (off site conservation)
In situ conservation: In situ means on site. It involves the protection of any species in its natural habitat. In this conservation stratagy we protects the animal in its original environmental ecololgy.
It can be done in following areas:
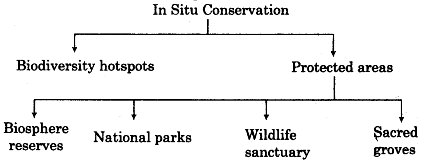
Boidiversity Hotspots: These are the specific areas with highest levels of species richness and high degree of endemism (which means that an endemic species does not found at any other place). Hotspots covers less than 2% of earth’s land area. There are 34 biodiversity hotspots in the world and in India there are 4 hotspots which are as follows:
- Wester Ghats
- Sri Lanka
- Sund Land
- Himalaya
Protected Areas: These are ecologically unique and biodiversitywise rich areas. These are called so because these are legally protected by their respective countries. Accordingly these are called:
- Biosphere reserves
- National Parks
- Sanctuaries
India has 14 biosphere reserves, 90 national parks and 448 wildlife sanctuaries.
Sacred Groves: These are basically the forest areas in particular which are set aside by the governments in order to protect the biodiversity. These many be religious and cultural places which are protected. For example,
Western ghat regions of kamataka and Maharasthtra. Khasi and Jaintia hills in Meghalaya.
Aravalli hills of Rajasthan.
Sarguja, Chanda and Bastar areas of Madhya Pradesh.
Ex Situ Conservation: In this conservation strategy threatened animals and plants are taken out from their natural habitats and they are placed in special care units for their protection and survival.
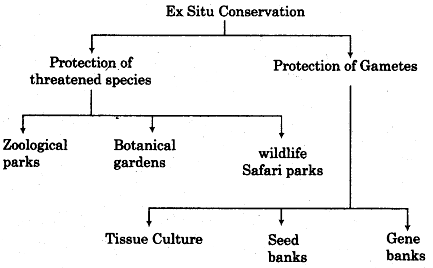
Cryopreservation: Cryopreservation means to preserve sperms, eggs, animal cells, tissue, seeds of different genetic strains and embryo at minus -190°C for longer times in viable and fertile conditions in gene banks, seed banks etc.
In Vitro Propagation: This method is used for plants propagation by using tissue culture techniques. In order to conserve an animal to save it from extinction a 3 way conservation strategy will be adopted.
