There are three types of cell division occurs in plants and animals. I. Amitosis, II. Mitosis, III. Meiosis.
I. Amitosis (Direct Nuclear Division): It is also called incipient or direct cell division. It is the most uncommon, primitive and simplest type of cell division. It is very rare and of little genetic importance. It is visible only in some unicellular organisms like bacteria, yeast, Amoeba, diatoms etc. It may also be seen in the higher plants but in some very old cells which are degenerating. This may be readegraded as a primitive form of mitosis.
Mechanism of Amitosis: It comprises two steps:
- (A) Karyokinesis
- (B) Cytokinesis
- (A) Karyokinesis: (Gk. karyon = nucleus, kinesis = movement), it involves division of nucleus. The nucleus starts elongating, thus a constriction appears approximately in the middle. The construction gradually deepens and eventually gives rise to two daughter nuclei. The two daughter nuclei thus formed are not equal in size.
- (B) Cytokinesis: It involves division of cytoplasm. In this stage, a constriction appears in the cytoplasm which divides it into two parts, each with a daughter nucleus. But the division of cytoplasm is not essential. Some times it does not occur after nuclear division. The result is multinucleate mass of protoplasm known as coenocyte and syncytium in case of plants and animals respectively.
(ii) Genetic Stability: Mitosis helps in the splitting of chromosomes during cell division and generates two new daughter cells. Therefore, the chromosomes form from the parent chromosome by copying the exact DNA. Therefore, the daughter cells formed as genetically uniform and identical to the parent as well as to each other. Thus, mitosis helps in preserving and maintaining the genetic stability of a particular population.
- Growth: Mitosis help in increasing the number of cells in a living organism thereby playing a significant role in the growth of a living organism.
- Replacement and Regeneration of New Cell: Regeneration and replacement of worn out and damaged tissues is a very important function of mitosis in living organisms. Mitosis helps in the production of identical copies of cells and thus helps in repairing the damaged tissue or replacing the worn out cells. But the degree of regeneration and replacement in multicellular organisms vary from one another. For example, mitosis process is used in order to regrowth the legs of newts and crustaceans.
- Asexual Reproduction: Mitosis is used in the production of genetically similar offspring. For example budding of Hydra and yeast, binary fission in Amoeba etc.
(iii)
|
Animal Cell Mitosis |
Plant Cell mitosis |
|
1. An animal cell becomes rounded before cell division. |
1. Plant cell do not change shape before the division. |
|
2. A number of hormones are known to induce cell division but a specific cell division hormone is not known. |
2. It is induced by a specific plant hormone called cytokinin. |
|
3. Centrosome is essential for it. |
3. Centrosome does not occur. |
|
4. Mitotic apparatus contains aster, spindle is amphiastral. |
4. Mitotic apparatus is without asters. Spindle is anastral. |
|
5. Spindle degenerates at the time of cytokinesis. |
5. A major part of spindle persists as phragmoplast at the time of cytokinesis. |
|
6. A mid body may be formed during cytokinesis. |
6. Mid body is absent. |
|
7. Cytokinesis occurs through cleavage. |
7. Cytokinesis occurs commonly by cell plate method. |
|
8. Microfilaments are involved in cytokinesis. |
8. Microfilaments do not seem to have any major function of cytokinesis. |
|
9. Cleavage proceeds centripetally. (from out to in). |
9. Cell plate grows centrifugally. (from in to out). |
|
10. A furrow is formed between two daughter cells. |
10. A solid middle lamella develops in between the two daughter cells for permanent adhesion. |
|
11. It occurs in bone marrow and many epithelial cells. |
11. It is found in meristematic cells. |
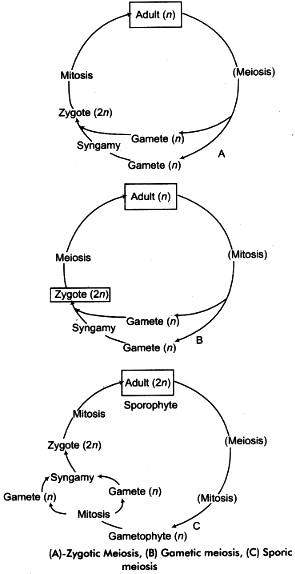
(iv) Depending upon the stage, when meiosis occur, the meiosis is of three types: Gametic, zygotic and sporic.
- Gametic or Terminal Meiosis: In most animals and some lower plants meiosis takes place during the formation of gametes (gametogenesis). Such a meiosis is described as gametic or terminal meiosis. When two gametes fuse to fertilisation, the diploid zygote is formed. Genetic meiosis results in diplontic life cycle.
- Zygotic or Initial Meiosis: In some lower plants meiosis takes place in the zygote and the resulting organisms are haploid. It is called zygotic or initial meiosis. Organisms having zygote meiosis have haplontic life cycle.
- Sporic or Intermediate Meiosis: In most of the plants, meiosis occur at the time of sporogenesis. It is called sporic or intermediate meiosis. Spore gives rise to a new gametophytic phase in the life cycle. The gametophyte produces gametes. The life of plant is said to be diplohaplontic because of the presence of diploid and haploid multicellular phases.