If r is the radius of the meniscus in the conical tube, then as shown in Fig.

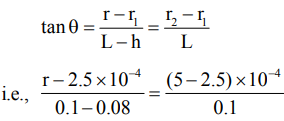
i.e., r × 104 – 2.5 = 0.2 × 2.5
i.e., r = 3 × 10–4 m
Now as capillarity is independent of the shape of tube so at same temp. θ = 0º C.

Now as from h= (2T/rρg) for cylindrical tube,
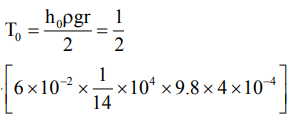
T0 = 8.4 × 10–2 N/m
Now as for a given tube and liquid T ∝ h (as T = hρgr/2)

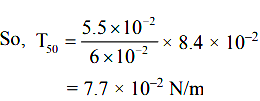
So rate of change of surface tension with temperature assuming linearity,
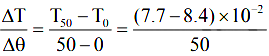
= –1.4 × 10–2 N/mºC
Negative sign shows that with rise in temperature surface tension decreases.