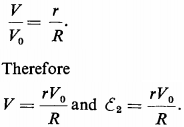Answer: ε2 = 1.8V.
Explanation:
The e.m.f. of the standard cell and of the accumulator give currents in opposite directions through the galvanometer. It is clear that the current ceases to flow in the galvanometer circuit when the difference of potential V across the ends of segment AB due to the standard cell is equal to the e.m.f. of the accumulator, i.e.,
V = ε2.
Since, in the case of a balanced circuit, there is no current in the galvanometer branch, it may be assumed that the potentials f the individual points of the potentiometer increase proportionally to the increase in the resistance of segment AB. i.e.,