Correct option (a, b, c, d)
Explanation:
Differentiability at x = 0
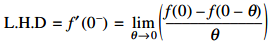
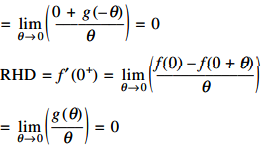
Thus, f(x) is differentiable at x = 0
Differentiability of h (x) at x = 0
h'(0+) = 1, h(x) is an even function.
Hence, non differentiable at x = 0
Differentiability of f(h (x)) at x = 0

since g'(1) ≠ 0, so f(h(x)) is non differentiable at x =
Differentiability of h ( f(x)) at x = 0
