Consider a uniform metallic wire XY of length l and cross sectional area A. A potential difference V is applied across the ends X andY of the wire. This causes an electric field at each point of the wire of strength
E = V/l. .....(1)
Due to this electric field, the electrons gain a drift velocity vd opposite to direction of electric field. If q be the charge passing through the cross-section of wire in t seconds, then current in wire I = q/t ......(2)
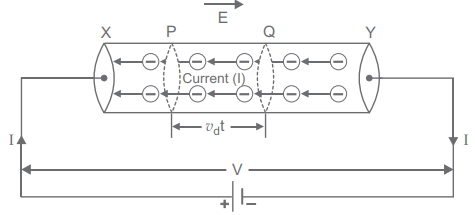
The distance traversed by each electron in time t
= average velocity x time =vdt
If we consider two planes P and Q at a distance vd t in a conductor, then the total charge flowing in time t will be equal to the total charge on the electrons present within the cylinder PQ.
The volume of this cylinder = cross-sectional area x height = Avdt
If n is the number of free electrons in the wire per unit volume, then the number of free electrons in the cylinder = n(Avdt) If charge on each electron is - e(e = 1.6 x 10-19C), then the total charge flowing through a cross-section of the wire
q = (nAvdt)(-e) = - neAvdt ......(3)
∴ Current flowing in the wire,
I =q/t = - (neAvdt)/t
i.e., current I = -neAvd .......(4)
This is the relation between electric current and drift velocity. Negative sign shows that the direction of current is opposite to the drift velocity
