Resistivity:
On practical basis it is found that the resistance depends upon the length l and area of cross-section A of the resistor as under
R ∝ \(\frac{l}{A}\)
or R = ρ\(\frac{l}{A}\)
where ρ = specific resistance or resistivity of the material of the conductor. It is the characteristic of the conductor.
Special fact: Resistivity does not depend upon the dimensions of the conductor i. e., it does not depend upon the length and area of cross-section of the conductor.
Effect of temperature on resistivity of metallic conductors:
Specific resistance is given by,
ρ = \(\frac{m}{n e^{2} \tau}\) ……………. (1)
Where, m = mass of electron
e = charge of electron
n = number of free electrons per unit volume
τ = relaxation time
In equation, there is no effect of increase in temperature on m and e. If temperature rise is not much, then n will also remain unchanged. Now we have to study the effect of rise in temperature on relaxation time τ.
∵ τ = \(\frac{\lambda}{v_{{rms}}}\)
Where λ is mean free path and vrms is the root mean square velocity of electrons.
When the temperature is increased, then the vibrational energy of atoms of the conductor increases and hence their amplitude of vibration increases and as result the value of mean free path λ decreases. Also due to increase in temperature the value of vrms increases. Hence due to combined effect of decrease in λ and increase in vrms, the relaxation time x will decrease. Thus it is clear from equation (1) the resistivity ρ will increase. Thus the specific resistance increases with increase in temperature. The change in resistivity (ρ) with rise in temperature is given by following relation,
ρt = ρ0(1 + αt) ………….(2)
Where ρt = Specific resistance at t°C
ρo = specific resistance at 0°C
α = linear temperature coefficient of resistance The variation in resistivity of metallic conductors with temperature is shown in figure.
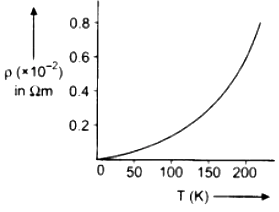
Temperature dependence of resistivity of semiconductor and insulator : Change in resistivity of semiconductor and insulator is different from change in resistivity of metallic conductors. For conductors the change in resistivity with temperature is linear but the change in resistivity of insulator
and semiconductor is represented by exponential curve as shown figure.

The mathematical variation of specific resistance with temperature
ρt = ρ0(1 – α Δt)
Linear temperature coefficient of resistivity is negative for semiconductor and conductors.
Resistivity of a semiconductor varies with temperature according to following relation :
\(\rho_{t}=\rho_{0} e^{-\left(\frac{E_{g}}{k T}\right)}\) …………. (3)
Where ρt = Resistivity at t°C
ρ0 = Resistivity at 0°C
Eg = Energy gap
k = Boltzmann constant
T = (273 + t°C) K