The tightly screwed lids or sealed bottles are first put in hot water so that the lid expands. In case of liquids, when the thermometer is put in a slightly warm water, the mercury in it rises. When the thermometer is taken out, mercury falls again.
In case of gases, a balloon partially inflated in a room (cool) expands when put in warm water. Also, a fully inflated balloon when placed in cold water starts shrinking.
Most of the substances expand on heating while contract on cooling. Change in the temperature of a body causes change in the dimensions of the body. The increase in dimensions of a body because of increase in its temperature is known as thermal expansion. The change in length is called linear expansion. The increase in area is called area expansion. The expansion in volume is called volume expansion.
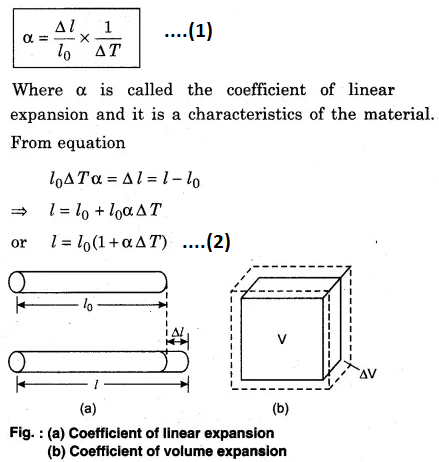
When the substance is in the form of a long rod, then for small change in temperature (∆T), the fractional change in length (∆l/l0) is directly proportional to ∆T.
Now, considering the fractional change in volume (\(\triangle V/V\)), the coefficient of volume expansion \(\beta\) is

where V is the initial volume of the substance. The unit of \(\alpha\) and \(\beta\) is K-1.
β is also a characteristic of the substance. Generally, it depends on the temperature. It becomes constant only at a high temperature. The value of β is more for those metals whose melting point is low. The value of β is least for solid, more than solids in liquids, maximum in gases.
From ideal gas equation, we know that

Now, we will establish the relation between α and β.
Consider a rectangular cuboid of length l1, l2 and l3 and on increasing the temperature by ∆T, the length changes to l‘1,l‘2 and l‘3 respectively. Then, according to equation.