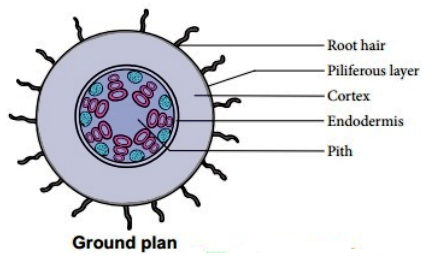
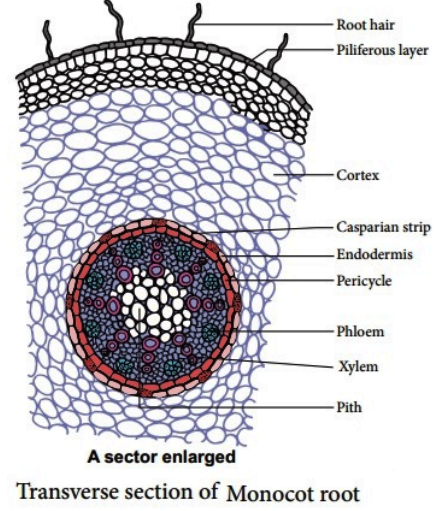
The internal structure of Monocot root has
1. Epiblema/Rhizodermis
2. Cortex
3. Endodermis
4. Stele
1. Epiblema/Rhizodermis:
- Outer most layer of monocot root.
- Made up of single layer of thin walled, paranchymatous cell.
- Root hair helps in absorption of water and minerals.
- Stomata and cuticle are absent.
- Main function is to protect inner tissue.
2. Cortex:
- The region below the epidermis is cortex.
- Made up of only parenchymatous cells with intercellular space.
- It is a multi layer.
- Function is to store water and food material.
3. Endodermis:
- Inner most cortex is called Endodermis.
- It forms a complete ring around the stele with characteristic Casparian strips and Passage cell.
- There is a band like thickening made of suberin in casparian strips.
(iv) Stele:
Central part inner to endodermis is stele. It contains Pericycle, vascular bundles and pith.
(a) Pericycle:
- Outer most layer of stele made of single layer of tightly arranged Parenchymatous cell.
- Function is to originate lateral root.
(b) Vascular bundles:
- Radial arrangement of vascular tissue.
- Xylem is exarch and polyarch
- The conjuctive tissue is sclerenchymatous tissue.
(c) Pith:
- Large central part, composed of parenchyma cells with intercellular spaces.
- Function is to store the starch.