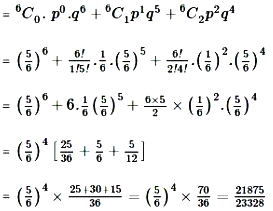The repeated throws of a die are Bernoulli trials.
Let X denotes the number of sixes in 6 throws of die.
Obviously, X has the binomial distribution with n = 6

where, p is probability of getting a six and q is probability of not getting a six
Now, Probability of getting at most 2 sixes in 6 throws
= P(X = 0) + P(X = 1) + P(X = 2)