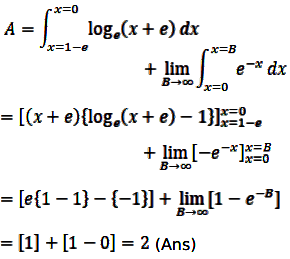Correct answer is A.
y =loge (x + e) and x = loge\(\left(\frac{1}{y}\right)\) look like –
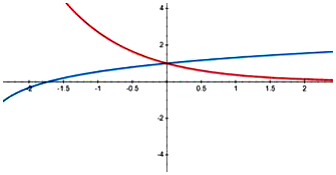
The curves intersect at (0, 1)
(Putting x = 0 in the 2 curves, y = loge (e) = 1 and 0 = loge (1/y),
i.e., y = 1/e0 = 1)
So, bounds are x = 1 – e to x = 0 for the first curve and then x = 0 to apparently x = ∞ for the second curve.
Therefore,