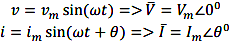Phasor Representation:
An alternating quantity can be represented using
i) Waveform
ii) Equations
iii) Phasor
A sinusoidal alternating quantity can be represented by a rotating line called a Phasor. A phasor is a line of definite length rotating in anticlockwise direction at a constant angular velocity.
The waveform and equation representation of an alternating current is as shown. This sinusoidal quantity can also be represented using phasors.
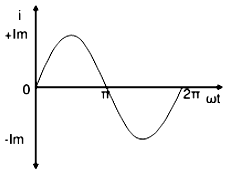
\(i=I_{m}\,sin\,\omega t\)
In phasor form the above wave is written as \(I^-=I_{m}\angle0^0\)
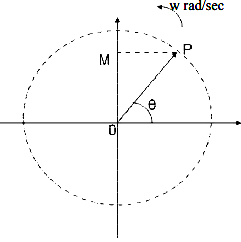
Draw a line OP of length equal to Im. This line OP rotates in the anticlockwise direction with a uniform angular velocity ω rad/sec and follows the circular trajectory shown in figure. At any instant, the projection of OP on the y-axis is given by OM=OPsinθ = Imsinωt. Hence the line OP is the phasor representation of the sinusoidal current.
Phase
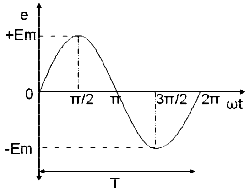
Phase is defined as the fractional part of time period or cycle through which the quantity has advanced from the selected zero position of reference.
Phase of +Em is π/2rad or T/4 sec
Phase of -Em is π/2rad or 3T/4 sec
Phase Difference

When two alternating quantities of the same frequency have different zero points, they are said to have a phase difference. The angle between the zero points is the angle of phase difference
In Phase
Two waveforms are said to be in phase, when the phase difference between them is zero. That is the zero points of both the waveforms are same. The waveform, phasor and equation representation of two sinusoidal quantities which are in phase is as shown. The figure shows that the voltage and current are in phase.

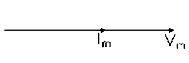
\(v=v_{m}\,sin(\omega t)\)
\(i=i_{m}\,sin(\omega t)\)
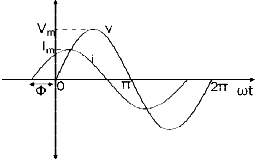
Lagging
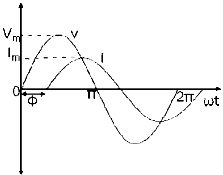
In the figure shown, the zero point of the current waveform is after the zero point of the voltage waveform. Hence the current is lagging behind the voltage. The waveform, phasor and equation representation is as shown.

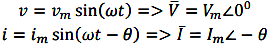
Leading
In the figure shown, the zero point of the current waveform is before the zero point of the voltage waveform. Hence the current is leading the voltage. The waveform, phasor and equation representation is as shown.