The concentration of either ‘A’ or ‘B’ was changed keeping the concentration of one of the reactants constant and rates were measured as a function of initial concentration following results were obtained. Find the order with respect to A and B and write the rate law for the reaction
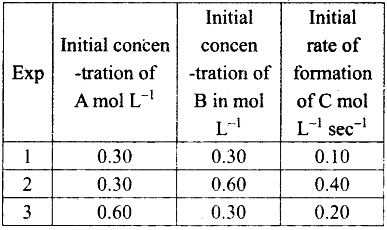
From experiments 1 and 3,
[B] = constant; [A] = doubled
rate is doubled.
Hence rate ∝ [A] i.e., the order with respect to A is 1.
From experiments 1, and 2,
[A] = constant; [B] doubled rate is quadrupled.
Hence, rate ∝ [B]2
i.e., order with respect by B is 2.
Combining rate = k [A] [B]2.