Superposition principle: It states that when a number of waves travelling simultaneously in the same medium overlap one another (superimpose), then the resultant displacement at any instant at any point in space is equal to the vector sum of the instantaneous displacements of individual waves.
if \(\overrightarrow y_1, \overrightarrow y_2,........\overrightarrow y_n\) are displacements of n individual waves at any instant, then the displacement of resultant wave \(\overrightarrow {y}\) will be
\(\overrightarrow {y} = \overrightarrow y_1 + \overrightarrow y_2+.......\overrightarrow y_n\)
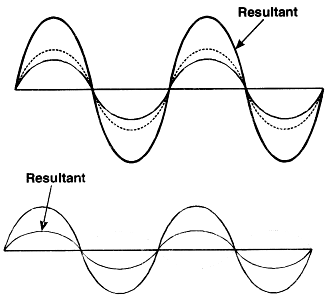
Consider two waves which are superimposing on each other as shown in Fig. If crest of one falls on the crest of other, the resultant amplitude will increase Fig. (a) and if crest of one falls on trough of other, the resultant amplitude will decrease Fig. (b). The principle of superposition is used to explain the interference of light.