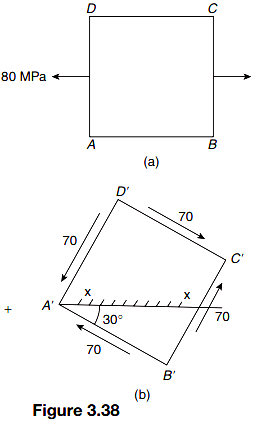
The state of stress at a point is the result of two separate actions: (i) one produces a tensile stress of 80 MPa in x-direction and (ii) the other produces a state of pure shear of 70 MPa as shown in Fig. 3.38. Find the resultant stress by rotating the state of stress in Fig. 3.38(b) to coincide with that of Fig. 3.38(a). Determine the principal stresses.