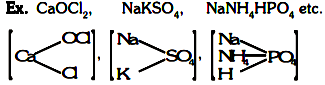The salts may be classified into four categories.
Simple salts :
The salts formed by the neutralisation process between acid and base.
These are of three types.
(i) Normal salt :
(i) The salt formed by the loss of all possible protons (replaceable H+ ions)
Ex: NaCl, NaNO3, K2SO4 , Ca3 (PO4)2, Na3 BO3, Na2 HPO3, NaH2 PO2 etc.
(ii) Acid salts :
(i) Salts formed by incomplete neutralisation of polybasic acids. Such salts contain one or more replaceable H atom.
Ex: NaHCO3 , NaHSO4 , NaH2 PO4, Na2 HPO4 etc.
(ii) Above salts when neutralized by base form normal salts.
(iii) Basic salts :
(i) Salts formed by in complete neutralisation of poly acidic bases are called basic salts. These salt contain one or more hydroxyl groups.
Ex: Zn(OH)Cl, Mg(OH)Cl, Fe(OH)2 Cl, Bi(OH)2 Cl etc.
(ii) Above salts when neutralised by acids form normal salts.
Double salts :
(i) The addition compounds formed by the combination of two simple salts are termed as double salts.
Ex: FeSO4 (NH4)2 SO4 . 6H2O (Ferrous ammonium sulphate), K2SO4 Al2 (SO4)3 .24H2O (Alum) and other alums.
(ii) Above salts are stable in solid state only.
(iii) When dissolved in water, it furnishes all the ions present in the simple salt from which it has been constituted.
(iv) The solution of double salt shows the properties of the simple salts from which it has been constituted.
Complex salts :
(i) These are formed by combination of simple salts or molecular compounds.
Ex:
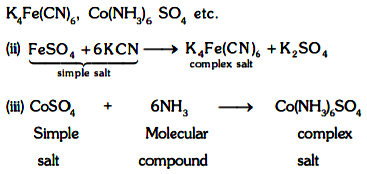
(iv) These are stable in solid states as well as in solutions.
(v) On dissolving in water, if furnishes a complex ion.
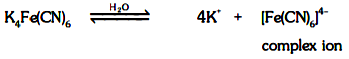
(vi) The properties of the solution are different from the properties of the substance from which it has been constituted.
Mixed salts :
(i) The salt which furnishes more than one cation or more than one anion when dissolved in water is called mixed salt.