One of the major problems of Carnot cycle is compressing a very wet steam mixture from the condenser pressure upto the boiler pressure. The problem can be avoided by condensing the steam completely in the condenser and then compressing the water in a comparatively small feed pump. The effect of this modification is to make the cycle practical one. Furthermore, far less work is required to pump a liquid than to compress a vapour and therefore this modification also has the result that the feed pump’s work is only one or two per cent of the work developed by the turbine. We can therefore neglect this term in our cycle analysis.
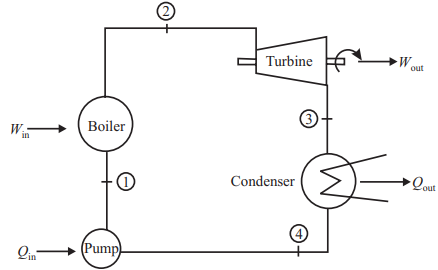
The idealized cycle for a simple steam power plant taking into account the above modification is called the Rankine cycle shown in the figure, Fig. It is made up of four practical processes:
(a) 1 - 2 :Heat is added to increase the temperature of the high-pressure water up to its saturation value (process 1 to A). The water is then evaporated at constant temperature and pressure (process A to 2). Both processes occur within the boiler, but not all of the heat supplied is at the maximum cycle temperature. Thus, the .mean temperature at which heat is supplied is lower than that in the equivalent Carnot cycle. Hence, the basic steam cycle thermal efficiency is inherently lower.Applying the first law of thermodynamics to this process:

(b) 2 - 3: The high pressure saturated steam is expanded to a low pressure within a reciprocating engine or a turbine. If the expansion is ideal (i.e., one of constant entropy), the cycle is called the Rankine cycle. However, in actual plant friction takes place in the flow of steam through the engine or turbine which results in the expansion with increasing entropy. Applying first law to this process:

(c) 3 - 4:The low-pressure ‘wet steam is completely condensed at constant condenser pressure back into saturated water. The latent heat of condensation is thereby rejected to the condenser cooling water which, in turn, rejects this heat to the atmosphere. Applying first law of the thermodynamics,

(d) 4 - 1:The low pressure saturated water is pumped back up to the boiler pressure and, in doing so, it becomes sub-saturated. The water then reenters the boiler and begins a new cycle. Applying the first law:

Specific steam consumption is given by:
