Venturimeter : This device is used to measure the rate of flow (or say flow speed) of the incompressible fluid flowing through a pipe. It works on the principle of Bernoulli’s theorem. It consists of two wider tubes A and A’ (with cross sectional area A) connected by a narrow tube B (with cross sectional area a). A manometer in the form of U-tube is also attached between the wide and narrow tubes. The manometer contains a liquid of density ‘ρm ’.
Let P1 be the pressure of the fluid at the wider region of the tube A. Let us assume that the fluid of density ‘ρ’ flows from the pipe with speed ‘v1 ’ and into the narrow region, its speed increases to ‘v2 ’. According to the Bernoulli’s equation, this increase in speed is accompanied by a decrease in the fluid pressure P2 at the narrow region of the tube B. Therefore, the pressure difference between the tubes A and B‘ is noted by measuring the height difference (∆P = P1 – P2 ) between the surfaces of the manometer liquid.
From the equation of continuity, we can say that Av1 = av2 which means that

From the above equation, the pressure difference
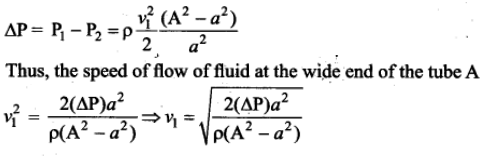
The volume of the liquid flowing out per second is
